
Teaching Biology involves using various methods that make learning scientific concepts engaging, practical, and understandable. Since Biology is a life science, it requires both theoretical understanding and hands-on experience. General teaching methods in Biology aim to help learners observe, explore, experiment, and analyze living organisms and life processes effectively.
Commonly used methods include lecture, discussion, demonstration, project, fieldwork, laboratory experiments, and inquiry-based learning. Each method is selected based on the topic, learners’ abilities, and available resources. For instance, laboratory work helps students develop scientific skills, while field trips connect classroom knowledge to real-life biological environments.
Overall, effective teaching of Biology integrates both teacher-centered and learner-centered approaches, encourages active participation, and develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and scientific inquiry skills essential for understanding life and the environment
Commonly used methods include lecture, discussion, demonstration, project, fieldwork, laboratory experiments, and inquiry-based learning. Each method is selected based on the topic, learners’ abilities, and available resources. For instance, laboratory work helps students develop scientific skills, while field trips connect classroom knowledge to real-life biological environments.
Overall, effective teaching of Biology integrates both teacher-centered and learner-centered approaches, encourages active participation, and develops critical thinking, problem-solving, and scientific inquiry skills essential for understanding life and the environment
- Teacher: EUSTINA Dr. MUDHUMO
- Teacher: Evangeline IRAKOZE
Natural resource management issues are inherently complex. They involve the ecological cycles, hydrological cycles, climate, animals, plants and geography, etc. All these are dynamic and inter-related. A change in one of them may have far reaching and/or long term impacts which may even be irreversible. In addition to the natural systems, natural resource management also has to manage various stakeholders and their interests, policies, politics, geographical boundaries, economic implications, etc. The management of natural resources over large spatial scales is inherently complex due to numerous biophysical and socioeconomic factors and the uncertainty associated with environmental systems and human behavior.
- Teacher: FELICIEN NIYONIRINGIYE
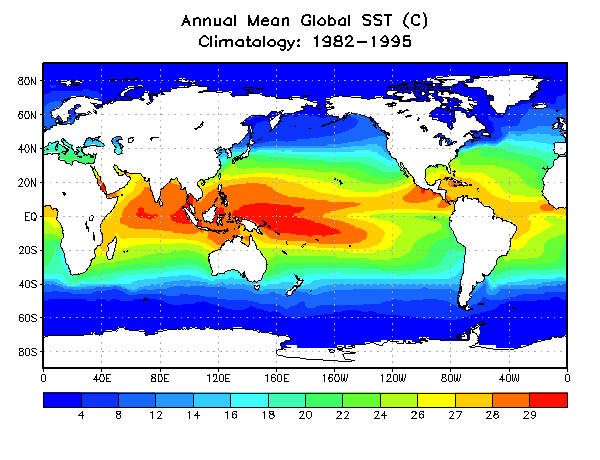
This module introduces students to the scientific study of climate and its variability across space and time. It examines the components and controls of the climate system, including solar radiation, atmospheric circulation, temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns. The course explores global and regional climate types, climate classification systems, and the interaction between climate and physical as well as human environments. Emphasis is placed on climate change, its causes, impacts, and adaptation and mitigation strategies, with particular reference to developing regions and Africa. Through lectures, data analysis, and practical applications, students develop skills in interpreting climatic data, understanding climate–environment relationships, and applying climatological knowledge to environmental management and sustainable development.
- Teacher: Dorcas ABAYISENGA
- Teacher: Dr. James OWINO
